Blankenbach benchmark
Thermal convection benchmark from Blankenbach et al., 1989
Initialize packages
Load JustRelax.jl necessary modules and define backend.
using JustRelax, JustRelax.JustRelax2D, JustRelax.DataIO
const backend_JR = CPUBackendFor this benchmark we will use particles to track the advection of the material phases and their information. For this, we will use JustPIC.jl
using JustPIC, JustPIC._2D
const backend = JustPIC.CPUBackend # Options: CPUBackend, CUDABackend, AMDGPUBackendWe will also use ParallelStencil.jl to write some device-agnostic helper functions:
using ParallelStencil
@init_parallel_stencil(Threads, Float64, 2) #or (CUDA, Float64, 2) or (AMDGPU, Float64, 2)and will use GeoParams.jl to define and compute physical properties of the materials:
using GeoParamsScript
Model domain
nx = ny = 51 # number of cells per dimension
nit = 6e3
igg = IGG(
init_global_grid(nx, ny, 1; init_MPI= true)...
) # initialize MPI grid
ly = 1.0 # domain length in y
lx = ly * ar # domain length in x
ni = nx, ny # number of cells
li = lx, ly # domain length in x- and y-
di = @. li / ni # grid step in x- and -y
origin = 0.0, 0.0 # origin coordinates
grid = Geometry(ni, li; origin = origin)
(; xci, xvi) = grid # nodes at the center and vertices of the cells
dt = dt_diff = 0.9 * min(di...)^2 / 4.0 # diffusive CFL timestep limiterRheology
rheology = (
SetMaterialParams(;
Phase = 1,
Density = PT_Density(; ρ0 = 1, α = 1, β = 0.0),
HeatCapacity = ConstantHeatCapacity(; Cp = 1.0),
Conductivity = ConstantConductivity(; k = 1.0),
CompositeRheology = CompositeRheology((LinearViscous(; η = 1),)),
RadioactiveHeat = ConstantRadioactiveHeat(0.0),
Gravity = ConstantGravity(; g = 1e4),
),
)Initialize particles
nxcell = 24 # initial number of perticles per cell
max_xcell = 35 # maximum number of perticles per cell
min_xcell = 12 # minimum number of perticles per cell
particles = init_particles(
backend, nxcell, max_xcell, min_xcell, xvi..., di..., ni...
) # particles object
subgrid_arrays = SubgridDiffusionCellArrays(particles) # arrays needed for subgrid diffusion
# velocity grids
grid_vx, grid_vy = velocity_grids(xci, xvi, di) # staggered velocity gridsand we want to keep track of the temperature pT, temperature of the previous time step pT0, and material phase pPhase:
pT, pT0, pPhases = init_cell_arrays(particles, Val(3))
particle_args = (pT, pT0, pPhases)Temperature anomaly
xc_anomaly = 0.0 # origin of thermal anomaly
yc_anomaly = 1 / 3 # origin of thermal anomaly
r_anomaly = 0.1 / 2 # radius of perturbationHelper function to initialize material phases with ParallelStencil.jl
function init_phases!(phases, particles)
ni = size(phases)
@parallel_indices (i, j) function init_phases!(phases, index)
@inbounds for ip in cellaxes(phases)
# quick escape if the ip-th element of the [i,j]-th cell is empty
@index(index[ip, i, j]) == 0 && continue
# all particles have phase number = 1.0
@index phases[ip, i, j] = 1.0
end
return nothing
end
@parallel (@idx ni) init_phases!(phases, particles.index)
end
init_phases!(pPhases, particles, lx, yc_anomaly, r_anomaly)or we can use the alternative one-liners
@views pPhase.data[!isnan.(particles.index.data)] .= 1.0or
map!(x -> isnan(x) ? NaN : 1.0, pPhase.data, particles.index.data)and finally we need the phase ratios at the cell centers:
phase_ratios = PhaseRatios(backend, length(rheology), ni)
update_phase_ratios!(phase_ratios, particles, xci, xvi, pPhases)Stokes and heat diffusion arrays
Stokes arrays object
stokes = StokesArrays(backend_JR, ni)and the correspondent heat diffusion one
thermal = ThermalArrays(backend_JR, ni)Initialize thermal profile and viscosity fields
To initialize the thermal profile we use ParallelStencil.jl again
@parallel_indices (i, j) function init_T!(T, y)
T[i, j] = 1 - y[j]
return nothing
end
@parallel (@idx size(thermal.T)) init_T!(thermal.T, xvi[2]) # cell vertices
@parallel (@idx size(thermal.Tc)) init_T!(thermal.Tc, xci[2]) # cell centersand we define a rectangular thermal anomaly at
function rectangular_perturbation!(T, xc, yc, r, xvi)
@parallel_indices (i, j) function _rectangular_perturbation!(T, xc, yc, r, x, y)
if ((x[i]-xc)^2 ≤ r^2) && ((y[j] - yc)^2 ≤ r^2)
T[i+1, j] += .2
end
return nothing
end
nx, ny = size(T)
@parallel (1:nx-2, 1:ny) _rectangular_perturbation!(T, xc, yc, r, xvi...)
return nothing
end
xc_anomaly = 0.0 # center of the thermal anomaly
yc_anomaly = 1/3 # center of the thermal anomaly
r_anomaly = 0.1/2 # half-width of the thermal anomaly
rectangular_perturbation!(thermal.T, xc_anomaly, yc_anomaly, r_anomaly, xvi)We initialize the buoyancy forces and viscosity
ρg = @zeros(ni...), @zeros(ni...)
η = @ones(ni...)
args = (; T = thermal.Tc, P = stokes.P, dt = Inf)
compute_ρg!(ρg[2], phase_ratios, rheology, args)
compute_viscosity!(stokes, 1.0, phase_ratios, args, rheology, (-Inf, Inf))where (-Inf, Inf) is the viscosity cutoff.
Boundary conditions
flow_bcs = VelocityBoundaryConditions(;
free_slip = (left = true, right=true, top=true, bot=true),
)
thermal_bc = TemperatureBoundaryConditions(;
no_flux = (left = true, right = true, top = false, bot = false),
)
thermal_bcs!(thermal, thermal_bc)
thermal.Told .= thermal.TPseuo-transient coefficients
pt_stokes = PTStokesCoeffs(li, di; ϵ_rel=1e-4, CFL = 1 / √2.1)
pt_thermal = PTThermalCoeffs(
backend_JR, rheology, phase_ratios, args, dt, ni, di, li; ϵ=1e-5, CFL = 1e-1 / √2.1
)Just before solving the problem...
We need to allocate some arrays to be able to do the subgrid diffusion of the temperature field at the particles level:
T_buffer = @zeros(ni.+1) # without the ghost nodes at the x-direction
Told_buffer = similar(T_buffer) # without the ghost nodes at the x-direction
dt₀ = similar(stokes.P) # subgrid diffusion time scale
# copy temperature to buffer arrays
for (dst, src) in zip((T_buffer, Told_buffer), (thermal.T, thermal.Told))
copyinn_x!(dst, src)
end
# interpolate temperatyre on the particles
grid2particle!(pT, xvi, T_buffer, particles)
pT0.data .= pT.datawhere
function copyinn_x!(A, B)
@parallel function f_x(A, B)
@all(A) = @inn_x(B)
return nothing
end
@parallel f_x(A, B)
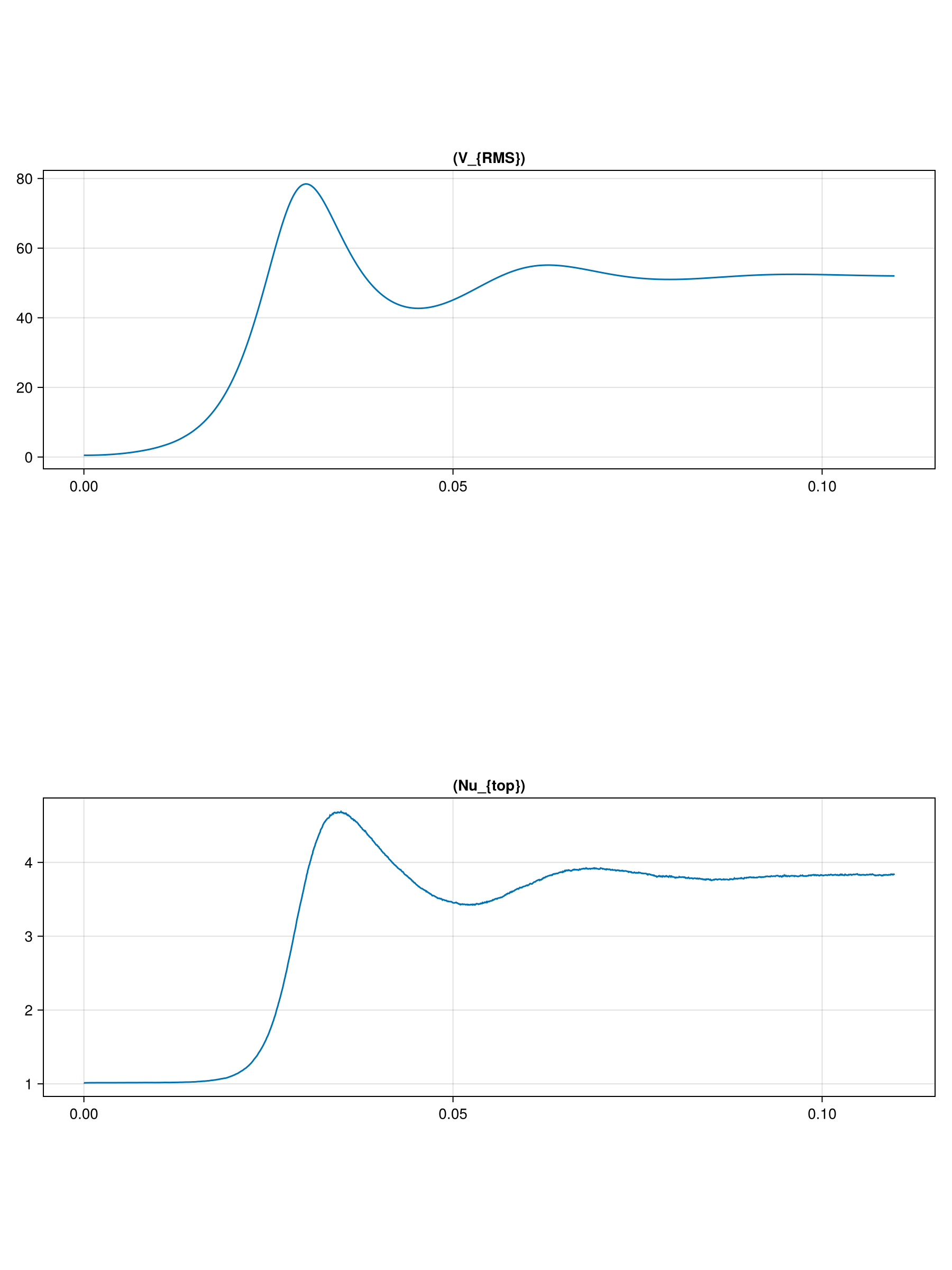
endIn this benchmark we want to keep track of the time trms, the rms-velocity Urms
and the Nusselt number at the top of the model Nu_top
And we will store their time history in the vectors:
Urms = Float64[]
Nu_top = Float64[]
trms = Float64[]We further need two buffer arrays where to interpolate the velocity field at the vertices of the grid cells
# Buffer arrays to compute velocity rms
Vx_v = @zeros(ni.+1...)
Vy_v = @zeros(ni.+1...)Advancing one time step
- Solve stokes
solve!(
stokes,
pt_stokes,
di,
flow_bcs,
ρg,
phase_ratios,
rheology,
args,
Inf,
igg;
kwargs = (;
iterMax = 150e3,
nout = 200,
viscosity_cutoff = (-Inf, Inf),
verbose = true
)
)
# calculate adaptive time step
dt = compute_dt(stokes, di, dt_diff)- Heat diffusion solver
heatdiffusion_PT!(
thermal,
pt_thermal,
thermal_bc,
rheology,
args,
dt,
di;
kwargs = (;
igg = igg,
phase = phase_ratios,
iterMax = 10e3,
nout = 1e2,
verbose = true,
)
)- Subgrid diffusion at the particle level
for (dst, src) in zip((T_buffer, Told_buffer), (thermal.T, thermal.Told))
copyinn_x!(dst, src)
end
subgrid_characteristic_time!(
subgrid_arrays, particles, dt₀, phase_ratios, rheology, thermal, stokes, xci, di
)
centroid2particle!(subgrid_arrays.dt₀, xci, dt₀, particles)
subgrid_diffusion!(
pT, T_buffer, thermal.ΔT[2:end-1, :], subgrid_arrays, particles, xvi, di, dt
)- Advect particles
# advect particles in space
advection!(particles, RungeKutta2(), @velocity(stokes), (grid_vx, grid_vy), dt)
# advect particles in memory
move_particles!(particles, xvi, particle_args)
# check if we need to inject particles
inject_particles_phase!(particles, pPhases, (pT, ), (T_buffer, ), xvi)
# update phase ratios
update_phase_ratios!(phase_ratios, particles, xci, xvi, pPhases)- Interpolate
Tback to the grid
# interpolate fields from particle to grid vertices
particle2grid!(T_buffer, pT, xvi, particles)
@views T_buffer[:, end] .= 0.0
@views T_buffer[:, 1] .= 1.0
@views thermal.T[2:end-1, :] .= T_buffer
flow_bcs!(stokes, flow_bcs) # apply boundary conditions
temperature2center!(thermal)- Update buoyancy forces and viscosity
args = (; T = thermal.Tc, P = stokes.P, dt=Inf)
compute_viscosity!(stokes, 1.0, phase_ratios, args, rheology, (-Inf, Inf))
compute_ρg!(ρg[2], phase_ratios, rheology, args)- Compute Nusselt number and rms-velocity
# Nusselt number, Nu = ∫ ∂T/∂z dx
Nu_it = sum( ((abs.(thermal.T[2:end-1,end] - thermal.T[2:end-1,end-1])) ./ di[2]) .*di[1])
push!(Nu_top, Nu_it)
# Compute U rms
# U₍ᵣₘₛ₎ = √ ∫∫ (vx²+vz²) dx dz
Urms_it = let
velocity2vertex!(Vx_v, Vy_v, stokes.V.Vx, stokes.V.Vy)
@. Vx_v .= hypot.(Vx_v, Vy_v) # we reuse Vx_v to store the velocity magnitude
sqrt(sum( Vx_v.^2 .* prod(di)) )
end
push!(Urms, Urms_it)
push!(trms, t)Visualization
We will use Makie.jl to visualize the results
using CairoMakieFields
# Make particles plottable
p = particles.coords
ppx, ppy = p
pxv = ppx.data[:]
pyv = ppy.data[:]
clr = pT.data[:]
idxv = particles.index.data[:];
# Make Makie figure
fig = Figure(size = (900, 900), title = "t = $t")
ax1 = Axis(fig[1,1], aspect = ar, title = "T [K] (t=$(t/(1e6 * 3600 * 24 *365.25)) Myrs)")
ax2 = Axis(fig[2,1], aspect = ar, title = "Vy [m/s]")
ax3 = Axis(fig[1,3], aspect = ar, title = "Vx [m/s]")
ax4 = Axis(fig[2,3], aspect = ar, title = "T [K]")
# grid temperature
h1 = heatmap!(ax1, xvi[1], xvi[2], Array(thermal.T[2:end-1,:]) , colormap=:lajolla, colorrange=(0, 1) )
# y-velocity
h2 = heatmap!(ax2, xvi[1], xvi[2], Array(stokes.V.Vy) , colormap=:batlow)
# x-velocity
h3 = heatmap!(ax3, xvi[1], xvi[2], Array(stokes.V.Vx) , colormap=:batlow)
# particles temperature
h4 = scatter!(ax4, Array(pxv[idxv]), Array(pyv[idxv]), color=Array(clr[idxv]), colormap=:lajolla, colorrange=(0, 1), markersize=3)
hidexdecorations!(ax1)
hidexdecorations!(ax2)
hidexdecorations!(ax3)
Colorbar(fig[1,2], h1)
Colorbar(fig[2,2], h2)
Colorbar(fig[1,4], h3)
Colorbar(fig[2,4], h4)
linkaxes!(ax1, ax2, ax3, ax4)
save(joinpath(figdir, "$(it).png"), fig)
figFinal model
Temperature field 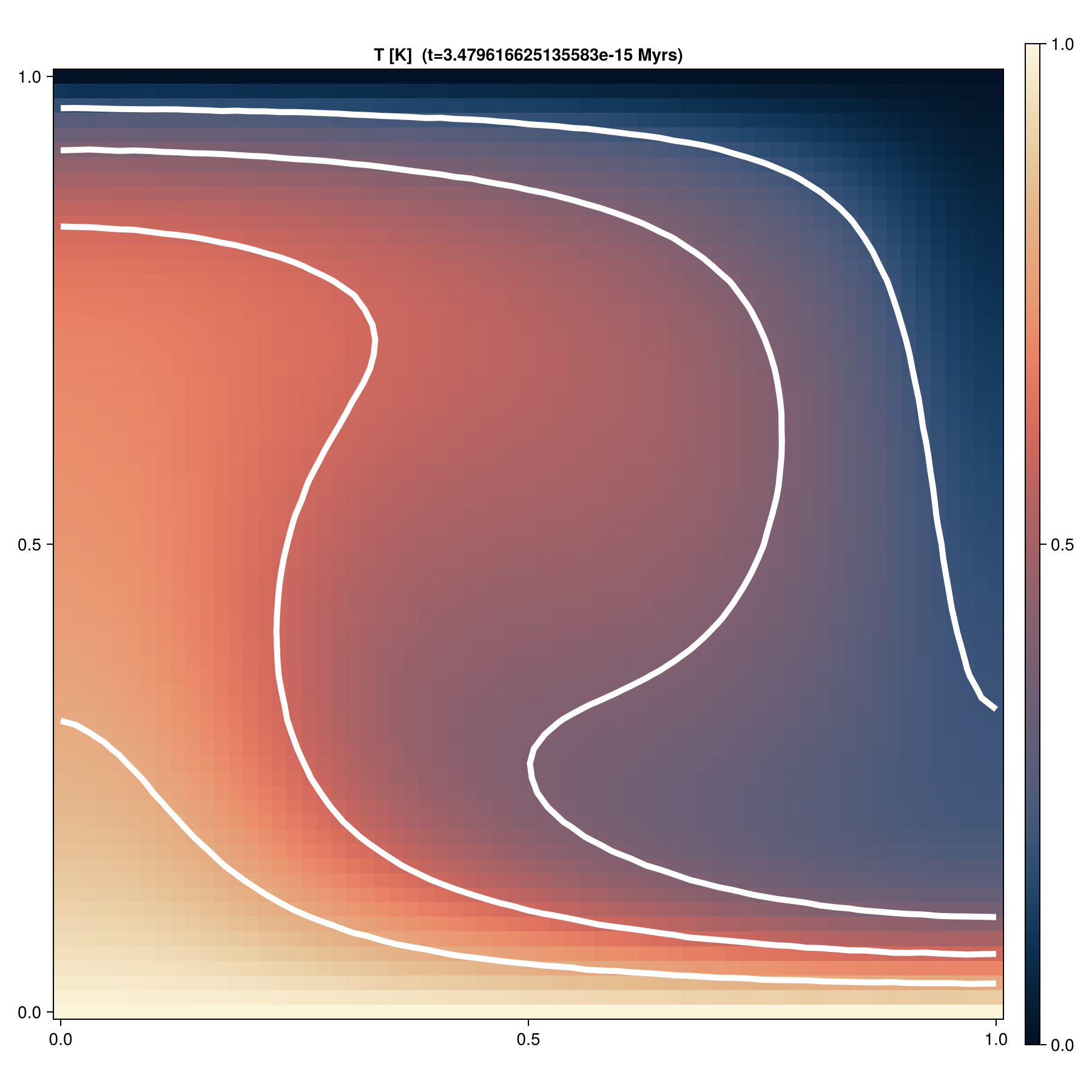
And time history of the rms-velocity and Nusselt number